Write the answer of each of the following questions :
(i) What is the name of horizontal and the vertical lines drawn to determine the position of any point in the Cartesian plane?
(ii) What is the name of each part of the plane formed by these two lines?
(iii) Write the name of the point where these two lines intersect.
Solution :
(i) The horizontal line is called the X-axis (or axis of abscissas), and the vertical line is called the Y-axis (or axis of ordinates).
(ii) Each of the four parts of the plane formed by the two intersecting lines is called a Quadrant.
(iii) The point where the X-axis and Y-axis intersect is called the Origin. It has the coordinates (0,0).
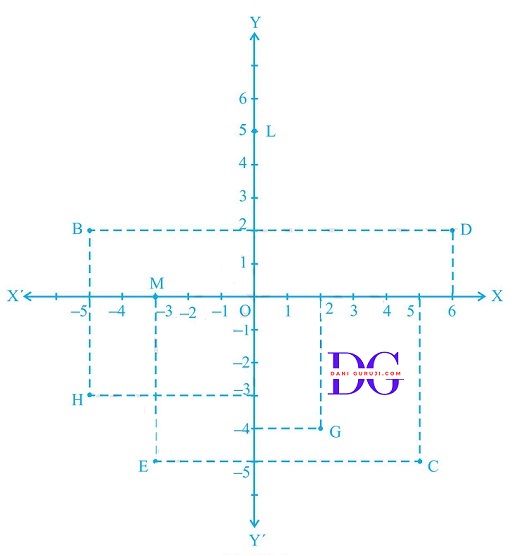
See figure, and write the following :
(i) The coordinates of B.
(ii) The coordinates of C.
(iii) The point identified by the coordinates (–3, –5).
(iv) The point identified by the coordinates (2, –4).
(v) The abscissa of the point D
(vi) The ordinate of the point H.
(vii) The coordinates of the point L.
(viii) The coordinates of the point M.
Solution :
(i) The coordinates of point B are the distance of point B from the x-axis and y-axis. Therefore, the coordinates of point B are (-5, 2).
(ii) The coordinates of point C are the distance of point C from the x-axis and y-axis. Therefore, the coordinates of point C are (5, -5).
(iii) The point that represents the coordinates (-3, -5) is E.
(iv) The point that represents the coordinates (2, -4) is G.
(v) The abscissa of point D is the distance of point D from the y-axis. Therefore, the abscissa of point D is 6.
(vi) The ordinate of point H is the distance of point H from the x-axis. Therefore, the abscissa of point H is -3.
(vii) The coordinates of point L in the above figure are the distance of point L from the x-axis and y-axis. Therefore, the coordinates of point L are (0, 5).
(viii) The coordinates of point M in the above figure are the distance of point M from the x-axis and y-axis. Therefore, the coordinates of point M are (-3, 0).
Syllabus for class 10
Advanced courses and exam preparation.
Previous Year Paper
Advanced courses and exam preparation.
Mock Test
Explore programming, data science, and AI.